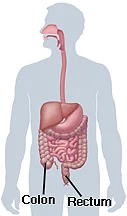
Cancer occurs when cells in the body begin changing and multiplying out of control. These cells can form lumps of tissue called tumors. Cancer that forms in the colon is called colon cancer. Cancer that forms in the rectum is called rectal cancer. These cancers are also called colorectal cancer.
Understanding the Colon and Rectum
The colon (also called the large intestine or large bowel) is a muscular tube that forms the last part of the digestive tract. It absorbs water and stores food waste. The colon is about 4 to 6 feet long. The rectum is the last 6 inches of the colon. The colon and rectum have a smooth lining composed of millions of cells. Changes in these cells can lead to growths in the colon that can become cancerous and should be removed.
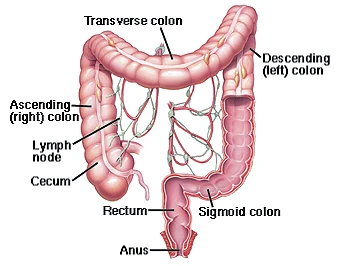
When the Colon Lining Changes
Changes that occur in the cells that line the colon or rectum can lead to growths called polyps. Over a period of years, polyps can turn cancerous. Removing polyps early may prevent cancer from ever forming.
- Polyps are fleshy clumps of tissue that form on the lining of the colon or rectum. Small polyps are usually benign (not cancerous). However, over time, cells in a polyp can change and become cancerous. The larger a polyp grows, the more likely this is to happen. Also, certain types of polyps known as adenomatous polyps are considered premalignant. This means that they will almost always become cancerous if they’re not removed.
- Colorectal cancers usually start when polyp cells begin growing abnormally. As a cancerous tumor grows, it may involve more and more of the colon or rectum. In time, cancer can also grow beyond the colon or rectum and spread to nearby organs or to glands called lymph nodes. The cells can also travel to other parts of the body. This is known as metastasis. The earlier a cancerous tumor is removed, the better the chance of preventing its spread.
Treatment Options for Colon and Rectal Cancer
You and your healthcare provider will discuss a treatment plan that’s best for your needs.
- Surgery is often done to remove the cancerous parts of the colon and rectum. Some surrounding tissue is removed as well, possibly including nearby lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy may be done in addition to surgery. This therapy uses medications to attack cancer cells. It is considered systemic therapy because it works throughout the body. It’s usually done as an outpatient procedure in a doctor’s office, clinic, or hospital. You may receive the medication in pill form or through an IV line or infusion pump (a device that slowly releases medication into your bloodstream).
- Radiation therapy may be done for rectal cancer. This treatment uses high-energy x-rays to kill cancer cells. It’s considered localized therapy because it targets the specific area of the body affected by the cancer. It is usually performed on an outpatient basis in a hospital or radiation clinic.
