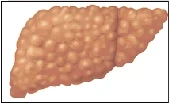
Cirrhosis is a chronic (long-lasting) liver problem. It results from damaged and scarred liver tissue. Cirrhosis can’t be cured, but it can be treated.
The Liver
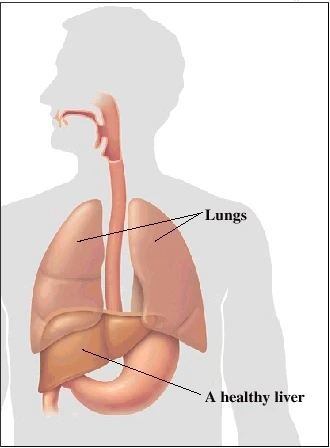
The liver is a large organ in the upper right part of the abdominal cavity. A healthy liver metabolizes proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Also, it makes a digestive fluid (bile), removes blood toxins, and is involved in the blood-clotting process.
When You Have Cirrhosis
Your liver becomes damaged and scarred when you have cirrhosis. And the liver doesn’t function as it should. In some cases, cirrhosis can lead to liver failure. If it does, your doctor will tell you whether you may need a liver transplant.
Causes of Cirrhosis
- Alcohol use
- Viral liver infections, such as hepatitis
- Chronic bile duct blockage
- Certain inherited diseases that can result in too much copper or iron being stored in the liver
- Certain medications
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Autoimmune disease
Common Signs and Symptoms
- Fatigue, weakness, and lack of appetite
- Vomiting with or without blood
- Weight loss or weight gain
- Yellowish skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Itching
- Swollen abdomen and legs
- Intestinal bleeding
- Easy bruising of the skin
- Dilated veins in the esophagus and stomach
- Poor mental function
